The Renaissance, a period of cultural rebirth that spanned roughly from the 14th to the 17th century, marked a significant turning point in the history of Western art. This era saw a renewed interest in classical learning and values, leading to revolutionary developments in painting, sculpture, and architecture. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore the key characteristics, influential artists, and enduring legacy of Renaissance art.
What is Renaissance Art?
Renaissance art refers to the painting, sculpture, and decorative arts produced during the Renaissance period, primarily in Italy and later spreading throughout Western Europe. The term “Renaissance” itself means “rebirth” in French, signifying the revival of classical culture and learning that characterized this era.
Key Characteristics of Renaissance Art:
- Realism and naturalism: Artists strived to depict the world as it truly appeared, with accurate proportions and perspective.
- Emphasis on the human form: The human body became a central subject, often portrayed in idealized forms.
- Use of perspective: Mathematical principles were applied to create the illusion of three-dimensional space on flat surfaces.
- Sfumato: A technique developed by Leonardo da Vinci, involving subtle gradations of light and shadow to create soft, hazy outlines.
- Chiaroscuro: The use of strong contrasts between light and dark to add drama and volume to compositions.
- Humanism: Art began to focus more on secular subjects and the individual, reflecting the humanist philosophy of the time.
The Early Renaissance (c. 1400-1490)
The Early Renaissance, centered in Florence, Italy, saw the first major shifts away from medieval artistic traditions. Artists began to experiment with new techniques and subjects, laying the groundwork for the High Renaissance to come.
Key Artists and Works:
- Masaccio (1401-1428): Considered the first great painter of the Early Renaissance, Masaccio’s frescoes in the Brancacci Chapel demonstrate his pioneering use of perspective and naturalistic figures (for more on Masterful Fresco technique read this).
- Fra Angelico (c. 1395-1455): Known for his serene and devout paintings, Fra Angelico’s work bridges the gap between the International Gothic style and the Early Renaissance.
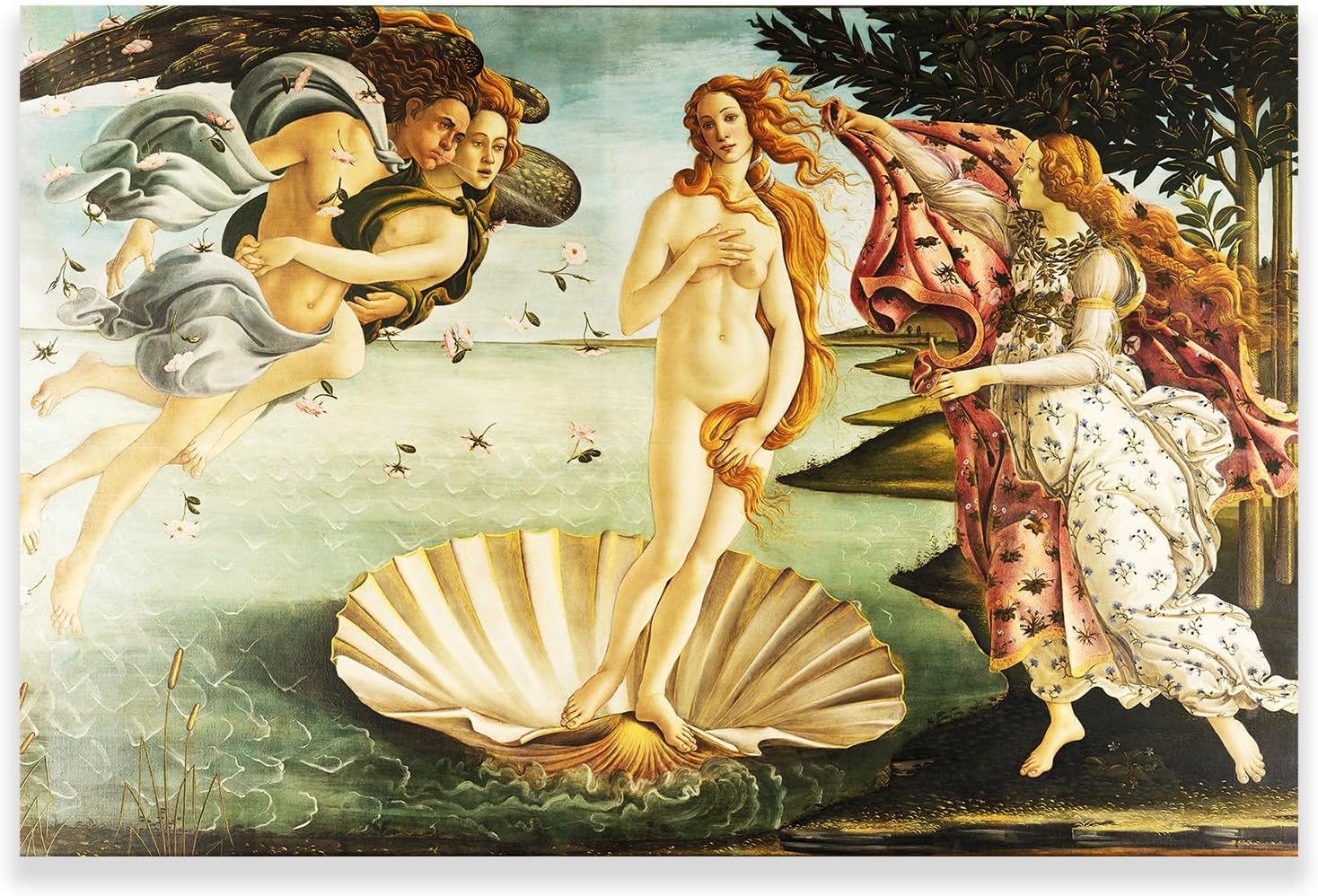
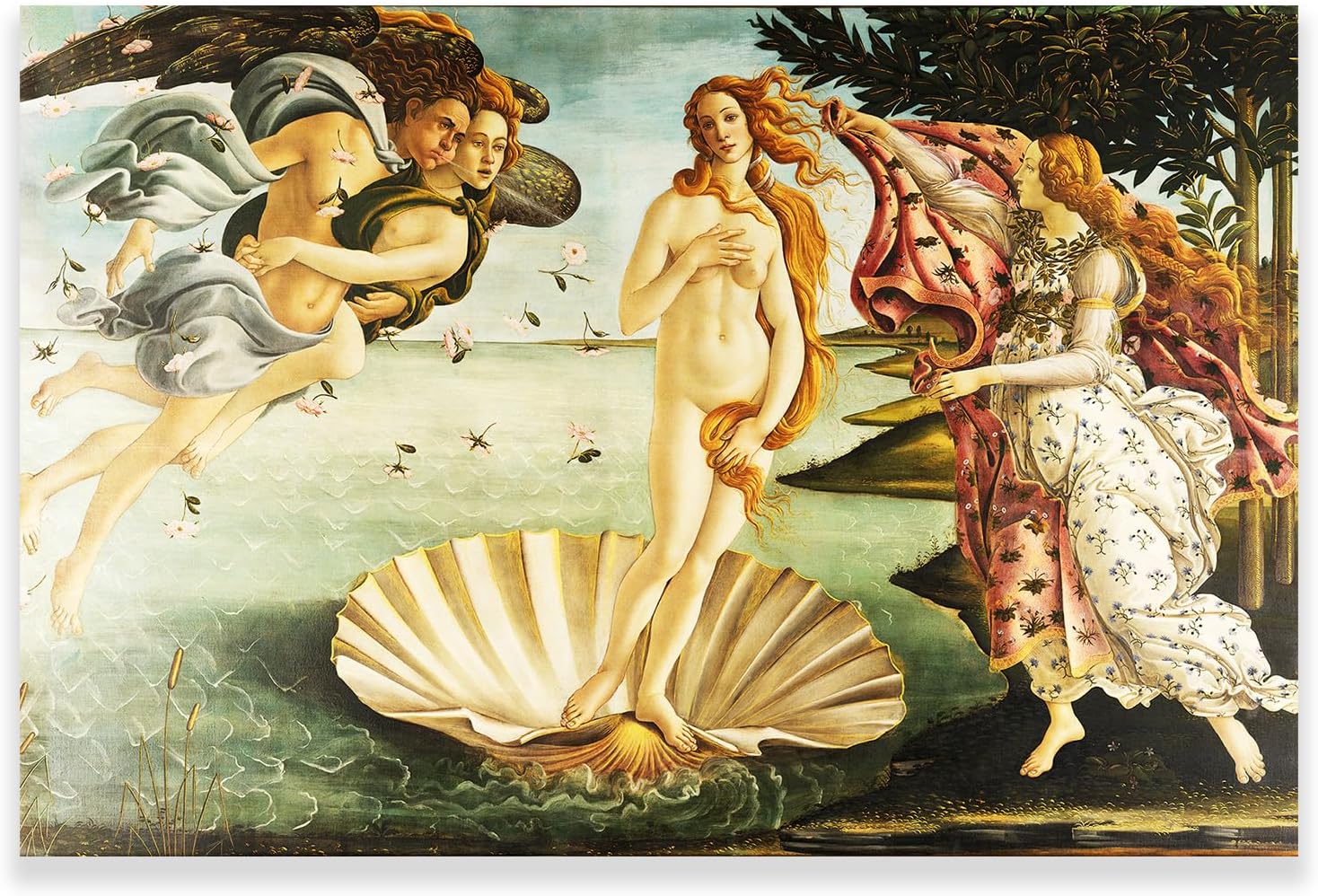
- Sandro Botticelli (1445-1510): Botticelli’s graceful, lyrical style is exemplified in works like “The Birth of Venus” and “Primavera,” which blend classical mythology with Christian symbolism.
The High Renaissance (c. 1490-1527)
The High Renaissance represents the pinnacle of artistic achievement during this period. Artists of this time created works of unparalleled beauty and technical mastery, often under the patronage of powerful figures like the Medici family and the Catholic Church.
The “Holy Trinity” of High Renaissance Artists:
- Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519):
- Known for: “Mona Lisa,” “The Last Supper”
- Contributions: Sfumato technique, anatomical studies, wide-ranging scientific and artistic explorations
- Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475-1564):
- Known for: Sistine Chapel ceiling, “David” sculpture
- Contributions: Mastery of human anatomy, powerful and dynamic figurative sculptures and paintings

- Raphael (1483-1520):
- Known for: “The School of Athens,” Vatican frescoes
- Contributions: Harmonious compositions, idealized beauty, synthesis of classical and Christian themes
Other Notable High Renaissance Artists:
- Titian (c. 1488-1576): Venetian master known for his use of color and sensual depictions of mythological subjects.
- Donato Bramante (1444-1514): Architect who designed St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome, exemplifying Renaissance architectural principles.
Northern Renaissance
While the Italian Renaissance was in full swing, Northern Europe experienced its own artistic revolution, influenced by, but distinct from, its southern counterpart.
Key Characteristics of Northern Renaissance Art:
- Greater emphasis on realism and detail
- Use of oil paints, allowing for richer colors and textures
- Focus on domestic scenes and landscapes
- Continued religious themes, influenced by the Protestant Reformation
Notable Northern Renaissance Artists:
- Jan van Eyck (c. 1390-1441): Flemish painter known for his meticulous detail and symbolic use of objects in works like “The Arnolfini Portrait.”
- Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528): German artist renowned for his printmaking and theoretical writings on art.
- Hieronymus Bosch (c. 1450-1516): Dutch painter famous for his fantastical and often nightmarish scenes, such as “The Garden of Earthly Delights.”

Renaissance Sculpture
Sculpture during the Renaissance period saw a revival of classical forms and techniques, with artists striving to capture the beauty and dynamism of the human form in three dimensions.
Key Sculptors and Works:
- Donatello (1386-1466): His bronze “David” is considered the first freestanding nude statue since antiquity.
- Lorenzo Ghiberti (1378-1455): Created the famous bronze doors of the Florence Baptistery, dubbed the “Gates of Paradise” by Michelangelo.
- Michelangelo: In addition to his paintings, Michelangelo was a master sculptor, creating works like “Pietà” and “David” that exemplify Renaissance ideals of beauty and emotion.
Renaissance Architecture
Renaissance architecture marked a conscious revival of elements of classical Roman and Greek architecture, emphasizing proportion, geometry, and the regularity of parts.
Key Principles of Renaissance Architecture:
- Use of classical orders (Doric, Ionic, Corinthian)
- Emphasis on symmetry and proportion
- Use of domes, particularly in church design
- Integration of classical elements like columns, pediments, and arches
Notable Architects and Buildings:
- Filippo Brunelleschi (1377-1446): Designed the dome of Florence Cathedral, a masterpiece of Renaissance engineering and aesthetics.
- Leon Battista Alberti (1404-1472): Wrote influential treatises on architecture and designed buildings like the Palazzo Rucellai in Florence.
- Andrea Palladio (1508-1580): His villas and churches, particularly in Venice and Vicenza, heavily influenced Western architecture for centuries.
The Legacy of Renaissance Art
The impact of Renaissance art extends far beyond its historical period, influencing artistic movements and cultural values up to the present day.
Enduring Influences:
- Artistic techniques: Many techniques developed during the Renaissance, such as linear perspective and sfumato, remain fundamental to Western art.
- Humanism: The Renaissance emphasis on individual achievement and the value of human experience continues to shape modern thought.
- Scientific inquiry: The detailed observational skills and curiosity of Renaissance artists contributed to advancements in anatomy, botany, and other sciences.
- Cultural education: Renaissance art remains a crucial part of cultural literacy, with works like the Mona Lisa and the Sistine Chapel ceiling being globally recognized icons.
- Architectural influence: Renaissance architectural principles continue to inform building design, particularly in government and institutional structures.
Conclusion
The Renaissance was a period of extraordinary artistic innovation and achievement, laying the foundation for much of Western art that followed. By blending classical influences with new techniques and a humanist philosophy, Renaissance artists created works of enduring beauty and significance. Whether you’re an art enthusiast or simply curious about this pivotal period in history, understanding Renaissance art opens up a world of visual splendor and intellectual depth.
As you continue to explore Renaissance art, consider visiting museums, studying art history books, or even planning a trip to Italy to see some of these masterpieces in person. The more you engage with these works, the more you’ll appreciate the skill, creativity, and cultural impact of Renaissance artists.
Remember, this guide is just the beginning. The world of Renaissance art is vast and endlessly fascinating, offering new discoveries and insights with each viewing. Happy exploring!