The world of painting encompasses an extraordinary diversity of art types and styles, each reflecting unique creative expressions and cultural influences. From classical realism to contemporary abstract expressionism, understanding the different types of artwork painting helps both artists and art enthusiasts appreciate the rich tapestry of visual art. Whether you’re exploring types of artistic painting for personal development or seeking to understand the various kinds of artists throughout history, this comprehensive guide will illuminate the fascinating spectrum of artistic expression.
Key Points Summary
• Classical Art Types: Realism, Renaissance, Baroque, and Neoclassical styles form the foundation of traditional painting
• Modern Art Styles: Impressionism, Expressionism, Cubism, and Surrealism revolutionized artistic expression
• Contemporary Movements: Abstract art, Pop Art, and Minimalism continue to shape current artistic trends
• Artist Classifications: Portrait artists, landscape painters, still-life specialists, and abstract artists represent different creative focuses
• Painting Techniques: Oil painting, watercolor, acrylic, and mixed media offer diverse artistic possibilities
• Cultural Influences: Regional art styles reflect local traditions, beliefs, and historical contexts
Understanding Different Type of Art Styles

Traditional and Classical Styles of Art
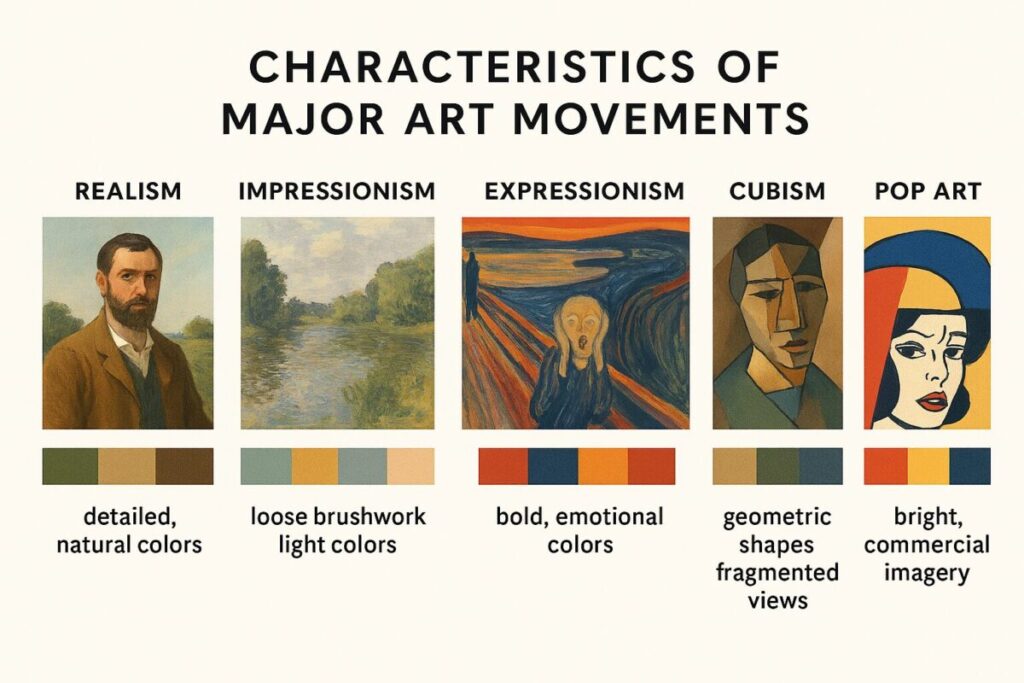
Realism represents one of the most fundamental types of art in painting, emphasizing accurate depiction of subjects without idealization. This artistic style emerged in the mid-19th century as artists sought to portray everyday life with unprecedented honesty. Realist painters focus on observable details, natural lighting, and authentic human experiences.
Renaissance Art stands among the most influential different types of styles in art, characterized by perspective, proportion, and humanistic themes. Masters like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo established techniques that continue influencing contemporary artists. This period introduced scientific approaches to anatomy, light, and composition.
Baroque Style emerged in the 17th century, featuring dramatic lighting, intense emotions, and dynamic movement. This types of artistic style emphasizes grandeur and spiritual intensity, often serving religious or royal patronage. Caravaggio’s chiaroscuro technique exemplifies Baroque’s dramatic light-dark contrasts.
Modern Artistic Movements
Impressionism revolutionized types of artwork painting by capturing fleeting moments and light effects. Artists like Monet and Renoir abandoned studio painting for outdoor observation, creating loose brushstrokes and vibrant color palettes that conveyed atmosphere over precise detail.
Expressionism prioritizes emotional content over realistic representation, making it one of the most psychologically intense styles of artwork. This movement includes German Expressionism and Abstract Expressionism, both emphasizing personal interpretation and emotional response.
Cubism, pioneered by Picasso and Braque, deconstructed objects into geometric forms, representing multiple perspectives simultaneously. This revolutionary approach to types of artistic painting challenged traditional representation methods and influenced countless subsequent movements.
Contemporary Art Classifications
Abstract Art encompasses various non-representational styles of art, from geometric abstraction to gestural expressionism. Abstract painters focus on color, form, and composition rather than recognizable subjects, creating purely visual experiences.
Pop Art emerged in the 1950s, incorporating popular culture imagery into fine art contexts. Artists like Andy Warhol transformed commercial imagery into types of art paintings that challenged traditional high-art boundaries.
Minimalism represents a reduction to essential elements, emphasizing simplicity and conceptual clarity. This types of artistic style strips away unnecessary details to focus on fundamental visual relationships.
Different Types of Artist Classifications

Specialized Artist Types
Portrait Artists specialize in human representation, capturing both physical likeness and psychological depth. This type of artist requires exceptional skill in anatomy, proportion, and character interpretation. Portrait painting spans from formal commissioned works to intimate personal studies.
Landscape Painters focus on natural environments, from pastoral scenes to dramatic wilderness depictions. These different types of artist interpret nature through various styles, from photorealistic detail to impressionistic interpretation.
Still Life Artists arrange and paint inanimate objects, exploring composition, color relationships, and symbolic meaning. This type of artists demonstrates technical mastery through careful observation of form, texture, and light.
Genre Painters depict everyday life scenes, capturing cultural moments and social interactions. These kinds of artists serve as visual historians, documenting human experiences across different periods and societies.
Contemporary Artist Categories
Abstract Artists work in non-representational modes, exploring pure visual elements without referential content. These types of artist push boundaries of traditional painting, often incorporating experimental materials and techniques.
Conceptual Artists prioritize ideas over traditional aesthetic concerns, using painting as a vehicle for intellectual exploration. This type of artists challenges conventional definitions of art and artistic value.
Mixed Media Artists combine traditional painting with other materials and techniques, creating hybrid artworks that transcend conventional categories. These different types of artist reflect contemporary art’s increasing interdisciplinary nature.
Art Styles and Techniques Comparison Table
| Art Style | Time Period | Key Characteristics | Famous Artists | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Realism | Mid-19th Century | Accurate depiction, natural lighting, everyday subjects | Gustave Courbet, Jean-François Millet | Portrait painting, social commentary |
| Impressionism | 1860s-1880s | Loose brushwork, light effects, outdoor painting | Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir | Landscape painting, capturing atmosphere |
| Expressionism | Early 20th Century | Emotional intensity, distorted forms, bold colors | Wassily Kandinsky, Franz Marc | Emotional expression, abstract concepts |
| Cubism | 1907-1920s | Geometric forms, multiple perspectives, fragmentation | Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque | Modern portraiture, still life |
| Abstract Art | 1910-Present | Non-representational, pure form and color | Jackson Pollock, Mark Rothko | Experimental painting, color studies |
| Pop Art | 1950s-1960s | Popular culture imagery, commercial techniques | Andy Warhol, Roy Lichtenstein | Contemporary themes, graphic elements |
| Minimalism | 1960s-Present | Simplicity, essential elements, geometric forms | Donald Judd, Agnes Martin | Clean compositions, conceptual work |
Regional and Cultural Art Types Painting

Western Artistic Traditions
European painting traditions encompass numerous styles of art, from Byzantine icons to Dutch Golden Age mastery. Each region developed distinctive approaches reflecting local culture, available materials, and patronage systems.
American painting evolved from colonial portraiture through Hudson River School landscapes to contemporary innovations. These types of art paintings reflect the nation’s cultural development and artistic independence.
Eastern Artistic Heritage
Asian painting traditions offer rich different types of styles in art, including Chinese ink painting, Japanese woodblock prints, and Indian miniature painting. These styles of artwork emphasize different aesthetic principles from Western traditions, often prioritizing spiritual expression and symbolic meaning.
Islamic art develops geometric patterns and calligraphic elements, creating types of artistic painting that reflect religious and cultural values while maintaining distinctive visual characteristics.
Technical Approaches in Types of Arts Painting

Traditional Media
Oil Painting remains fundamental among types of art in painting, offering exceptional blending capabilities and archival permanence. This medium supports both detailed realism and expressive abstraction, making it versatile for various artistic styles.
Watercolor creates luminous, transparent effects unique among different type of art styles. This challenging medium requires confident brushwork and understanding of water behavior, producing spontaneous and atmospheric results.
Tempera represents one of the oldest types of artistic painting, using egg yolk as a binder. This medium creates precise details and brilliant colors, favored by early Renaissance masters.
Contemporary Materials
Acrylic Paint offers fast-drying versatility, supporting both traditional and experimental approaches. These modern materials enable new types of artwork painting previously impossible with traditional media.
Mixed Media combines various materials and techniques, creating innovative styles of art that reflect contemporary artistic freedom and experimentation.
Understanding Artistic Development
Historical Evolution
Art styles evolved through cultural, technological, and philosophical changes. Understanding this progression helps appreciate how different types of artist responded to their historical contexts while developing new visual languages.
Individual Artistic Journey
Every type of artists develops personal style through training, experimentation, and creative exploration. This individual development process creates the diversity we see in contemporary types of art paintings.
Cultural Exchange
Globalization enables unprecedented exchange between different types of styles in art, creating hybrid approaches that blend traditional and contemporary influences.
Master Artists and Their Signature Styles
| Artist Name | Primary Art Style | Nationality/Period | Signature Technique | Famous Works | Type of Artist Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leonardo da Vinci | High Renaissance | Italian, 1452-1519 | Sfumato (soft shading), scientific accuracy | Mona Lisa, The Last Supper | Portrait artist, inventor, polymath |
| Vincent van Gogh | Post-Impressionism | Dutch, 1853-1890 | Bold brushstrokes, emotional color | Starry Night, Sunflowers | Landscape/still life artist |
| Pablo Picasso | Cubism, Blue Period | Spanish, 1881-1973 | Geometric fragmentation, multiple perspectives | Les Demoiselles d’Avignon, Guernica | Abstract artist, revolutionary innovator |
| Claude Monet | Impressionism | French, 1840-1926 | Plein air painting, light studies | Water Lilies, Impression Sunrise | Landscape artist, light specialist |
| Jackson Pollock | Abstract Expressionism | American, 1912-1956 | Drip painting, action painting | No. 1 (Lavender Mist), Autumn Rhythm | Abstract artist, gestural painter |
| Georgia O’Keeffe | American Modernism | American, 1887-1986 | Close-up natural forms, color abstraction | Black Iris, Cow’s Skull | Nature artist, color specialist |
| Frida Kahlo | Surrealism/Mexican Folk | Mexican, 1907-1954 | Symbolic self-portraiture, cultural imagery | The Two Fridas, Self-Portrait with Thorn | Portrait artist, surrealist |
| Andy Warhol | Pop Art | American, 1928-1987 | Screen printing, commercial imagery | Campbell’s Soup Cans, Marilyn Diptych | Pop artist, commercial innovator |
| Johannes Vermeer | Dutch Golden Age | Dutch, 1632-1675 | Light mastery, domestic scenes | Girl with a Pearl Earring, The Milkmaid | Genre painter, light artist |
| Wassily Kandinsky | Abstract Art/Expressionism | Russian, 1866-1944 | Color theory, spiritual abstraction | Composition VII, Yellow-Red-Blue | Abstract artist, color theorist |
| Henri Matisse | Fauvism/Modernism | French, 1869-1954 | Bold color, paper cut-outs | Woman with a Hat, The Dance | Color artist, decorative painter |
| Caravaggio | Baroque | Italian, 1571-1610 | Chiaroscuro (dramatic light/dark) | The Calling of St. Matthew, Judith Beheading Holofernes | Religious painter, naturalist |
| Jean-Michel Basquiat | Neo-Expressionism | American, 1960-1988 | Graffiti-inspired, social commentary | Untitled (Skull), Hollywood Africans | Street artist, social commentator |
| Yves Klein | Conceptual Art | French, 1928-1962 | Monochrome painting, International Klein Blue | Anthropometry series, IKB paintings | Conceptual artist, color innovator |
| Katsushika Hokusai | Japanese Ukiyo-e | Japanese, 1760-1849 | Woodblock printing, landscape series | The Great Wave, Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji | Landscape artist, printmaker |
Conclusion
The vast landscape of art types and styles reflects humanity’s diverse creative expression throughout history. From traditional realism to contemporary abstraction, each styles of artwork offers unique perspectives and aesthetic experiences. Understanding these different types of artist classifications and their corresponding styles of art enriches our appreciation for painting’s continuing evolution. Whether you’re an aspiring artist exploring various types of artistic painting or an enthusiast seeking deeper understanding, recognizing these distinctions enhances your engagement with visual art’s rich heritage and exciting future possibilities.
FAQs: Guide to Art Types and Styles
What are the main types of art styles in painting?
The main art styles include Realism, Impressionism, Expressionism, Cubism, Abstract art, Pop Art, and Minimalism. Each style represents different approaches to color, form, composition, and subject matter representation.
How many different types of artists are there?
Artists can be classified by specialization (portrait, landscape, still life), medium (oil, watercolor, acrylic), style (realistic, abstract, impressionistic), or cultural tradition (Western, Eastern, Indigenous). The categories are numerous and often overlapping.
What’s the difference between art types and art styles?
Art types typically refer to broad categories like painting, sculpture, or drawing, while art styles refer to specific approaches within those types, such as Impressionism or Cubism in painting.

Which art style is easiest for beginners?
Realism and Impressionism are often recommended for beginners because they provide clear reference points and established techniques. However, the “easiest” style depends on individual interests and natural inclinations.
How do I identify different painting styles?
Look for characteristic elements: brushwork (loose vs. tight), color palette (muted vs. vibrant), subject matter (realistic vs. abstract), and composition (traditional vs. experimental). Historical period and cultural context also provide important clues.
What determines an artist’s style?
An artist’s style develops through training, personal preferences, cultural influences, available materials, and individual creative exploration. Most artists evolve their style throughout their careers.
Citations
- Gardner, Helen. “Gardner’s Art Through the Ages: A Global History.” Cengage Learning, 2020.
- Janson, H.W. “Janson’s History of Art: The Western Tradition.” Pearson, 2019.
- Kleiner, Fred S. “Gardner’s Art Through the Ages: Backpack Edition.” Cengage Learning, 2018.
- Stokstad, Marilyn. “Art History.” Pearson, 2017.
- Metropolitan Museum of Art. “Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History.” metmuseum.org
- National Gallery of Art. “NGA Online Editions.” nga.gov
- Tate Modern. “Art Terms and Techniques.” tate.org.uk
- Museum of Modern Art. “Collection Database.” moma.org


