Understanding art styles has never been more fascinating than it is today. With artificial intelligence revolutionizing how we analyze masterpieces, art styles explained through machine learning reveals patterns and distinctions that even trained art historians might miss. From the precise brushstrokes of Renaissance masters to the bold color explosions of Fauvism, AI technology is transforming our appreciation of artistic movements while making art education more accessible than ever before.
Key Takeaways
• AI technology can identify subtle patterns in brushstrokes, color composition, and artistic techniques that distinguish different art movements
• Classical art styles like Renaissance and Baroque evolved through specific historical contexts and technical innovations
• Modern art movements from Impressionism to Abstract Expressionism represent revolutionary changes in artistic vision and technique
• Machine learning algorithms analyze thousands of data points to authenticate artwork and detect forgeries
• Understanding art styles enhances personal appreciation and helps identify valuable pieces in collections
Art Styles Explained
The world of art encompasses countless styles, each with distinct characteristics that reflect the cultural, social, and technological context of their time. When we examine art styles explained through both traditional art history and modern AI analysis, we discover layers of meaning that make each movement unique and revolutionary.
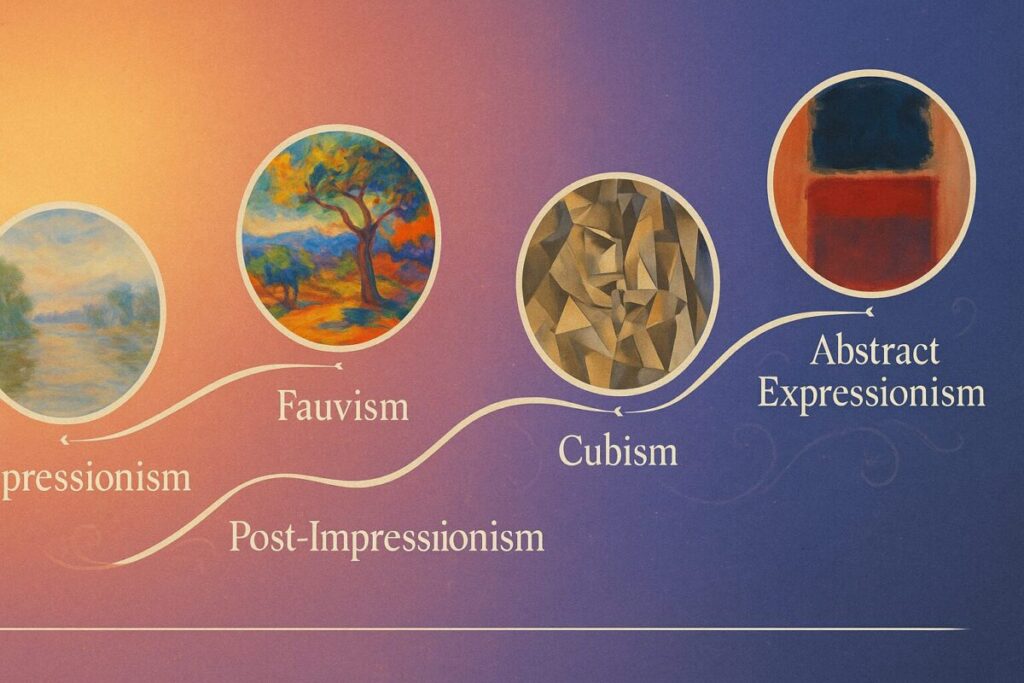
Art styles represent more than just different ways of painting—they embody philosophical approaches to representing reality, emotion, and human experience. From the mathematical precision of Renaissance perspective to the emotional intensity of Expressionism, each style tells a story about humanity’s evolving relationship with visual representation.
Classical Art Styles: Foundation of Western Art
Classical art styles laid the groundwork for virtually every subsequent artistic movement. The Renaissance period, spanning roughly from the 14th to 17th centuries, emphasized realistic representation through mathematical perspective and careful observation of light and shadow. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci perfected techniques such as sfumato, creating soft gradations between colors and tones.
The Baroque period followed, introducing dramatic lighting effects known as chiaroscuro and emotional intensity that contrasted sharply with Renaissance calm. Caravaggio’s revolutionary use of light and shadow created paintings that seemed to glow from within, influencing artists for centuries to come. Understanding these classical art styles provides essential context for appreciating later developments.
Neoclassicism emerged in the 18th century as a reaction against Baroque excess, returning to classical Greek and Roman ideals of beauty and proportion. Artists like Jacques-Louis David created works with clean lines, noble subjects, and moral messages that reflected Enlightenment values. This movement demonstrates how art movements explained through historical context reveals deeper cultural meanings.

Modern Art Movements: Revolutionary Changes
The transition from classical to modern art represents one of the most dramatic shifts in human creative expression. Impressionism, beginning in the 1860s, broke away from academic traditions by focusing on light, color, and the fleeting effects of atmosphere. Claude Monet and his contemporaries painted outdoors, capturing natural light with loose brushstrokes that scandalized critics but delighted audiences.
When examining characteristics of Impressionism, we see how artists prioritized visual sensation over detailed representation. This revolutionary approach paved the way for Post-Impressionism, where artists like Vincent van Gogh and Paul Cézanne pushed color and form even further from naturalistic representation.
| Art Movement | Time Period | Key Characteristics | Notable Artists |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impressionism | 1860s-1880s | Light effects, loose brushwork, outdoor painting | Monet, Renoir, Degas |
| Post-Impressionism | 1880s-1900s | Emotional expression, bold colors, symbolic content | Van Gogh, Cézanne, Gauguin |
| Fauvism | 1905-1910 | Wild colors, simplified forms, emotional intensity | Matisse, Derain, Vlaminck |
| Cubism | 1907-1920s | Geometric forms, multiple perspectives, fragmentation | Picasso, Braque, Gris |
The geometric revolution of Cubism represents perhaps the most radical departure from traditional representation. Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque deconstructed objects into geometric shapes, showing multiple viewpoints simultaneously and challenging fundamental assumptions about how art should represent reality.
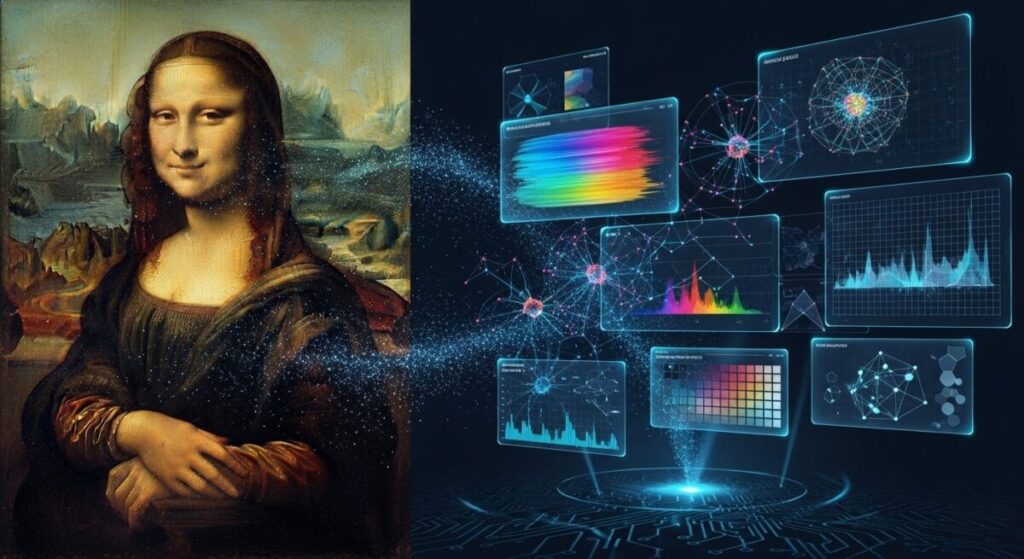
AI’s Revolutionary Role in Art Analysis

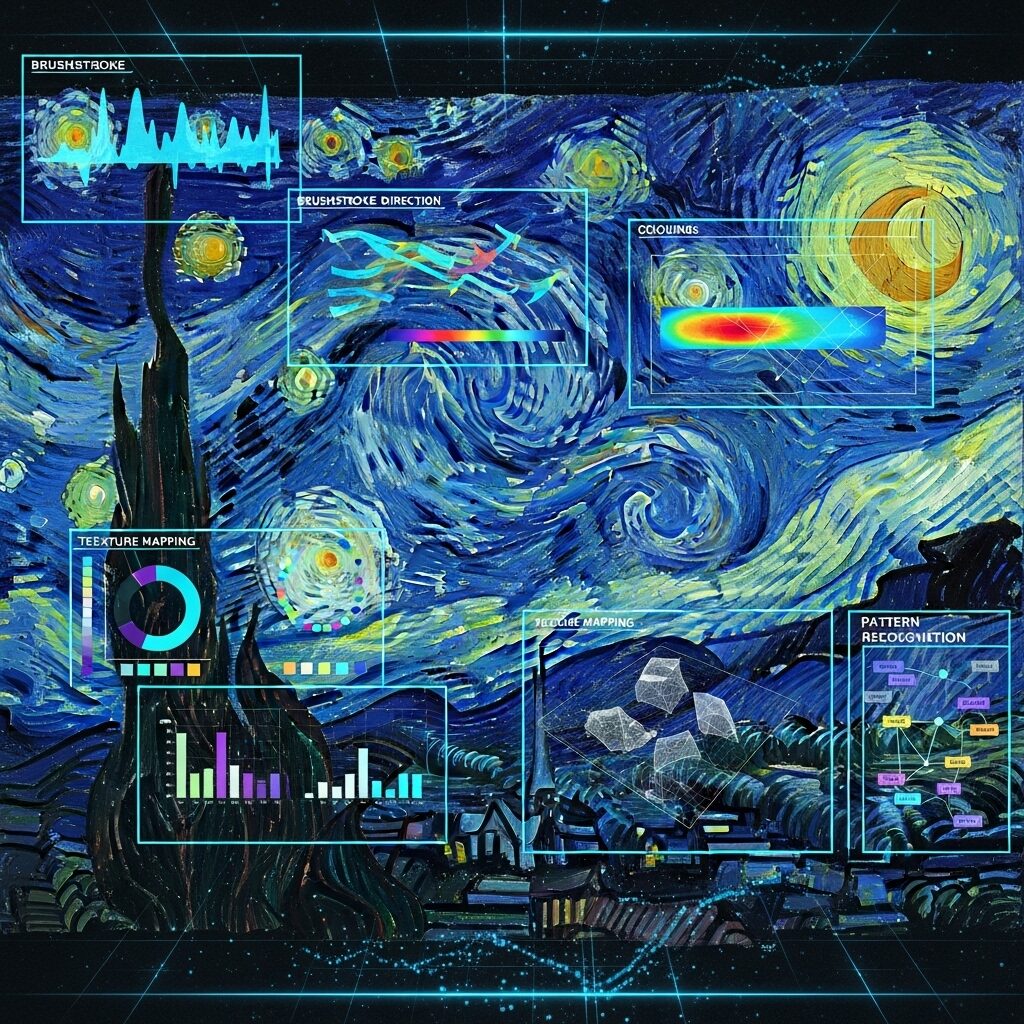
Artificial intelligence has transformed how we understand and analyze art styles. Machine learning algorithms can process thousands of paintings, identifying subtle patterns in brushstrokes, color palettes, and compositional elements that distinguish different movements and individual artists. This technology provides unprecedented insights into artistic techniques and helps authenticate works that might otherwise remain mysteries.
Modern AI systems analyze multiple data points simultaneously, including brushstroke direction, paint thickness, color temperature, and compositional balance. When examining AI’s impact on artistic creation, we see how these tools complement rather than replace human expertise, providing quantitative analysis that supports art historical research.
“AI doesn’t replace the human eye and trained expertise—it enhances our ability to see patterns and connections that might otherwise remain hidden. The technology serves as a powerful tool for both scholars and art lovers seeking deeper understanding of masterpieces.”
Dr. Sarah Chen, Art History Professor and AI Research Specialist
Computer vision technology can detect forgeries by analyzing paint layers, aging patterns, and microscopic details invisible to the naked eye. These practical AI art analysis tools are revolutionizing museums, auction houses, and private collections worldwide.
Identifying Distinctive Characteristics
Learning to learn to identify different art movements requires understanding the specific visual elements that define each style. Renaissance paintings feature mathematical perspective, realistic proportions, and careful attention to light and shadow. Baroque works emphasize dramatic contrasts, emotional intensity, and dynamic compositions that draw viewers into the scene.
Impressionist paintings are characterized by visible brushstrokes, emphasis on natural light, and subjects painted outdoors. The paint often appears fresh and spontaneous, with colors mixed optically rather than on the palette. Post-Impressionist works push these concepts further, using color and form for emotional expression rather than realistic representation.
Modern movements each developed unique visual languages. Matisse’s revolutionary Fauvism techniques emphasized pure color over naturalistic representation, while Cubism fragmented objects into geometric planes. Abstract Expressionism abandoned representational subjects entirely, focusing on pure emotion expressed through color, gesture, and form.

Practical Applications and Authentication
Understanding art styles serves practical purposes beyond aesthetic appreciation. Art authentication relies heavily on stylistic analysis, comparing questionable works against established characteristics of specific artists and movements. Professional authenticators use both traditional connoisseurship and modern technology to verify attributions.
Museums and galleries employ stylistic analysis for cataloging collections, planning exhibitions, and educating visitors. The ability to explore famous artist styles helps curators create meaningful connections between different works and movements.
Private collectors benefit from understanding art styles when building collections or evaluating potential purchases. Knowledge of stylistic characteristics helps identify valuable pieces, avoid forgeries, and appreciate the historical significance of artworks. This practical application makes art education valuable for both professional and personal purposes.
| Authentication Method | Technology Used | Accuracy Rate | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brushstroke Analysis | AI Pattern Recognition | 94% | Attribution verification |
| Pigment Analysis | Spectroscopy | 98% | Dating and authenticity |
| Canvas Dating | Radiocarbon testing | 95% | Historical verification |
| Style Comparison | Machine learning | 92% | Movement classification |
Building Your Art Appreciation Skills

Developing expertise in recognizing art styles enhances museum visits, gallery experiences, and personal collecting. Start by studying the master painters and their distinctive techniques, focusing on how different artists solved similar artistic problems through their unique approaches.
Practice comparing similar works from different periods or movements. Notice how Renaissance artists used linear perspective differently than Baroque artists employed atmospheric perspective. Observe how Impressionists captured light compared to Post-Impressionists’ emotional use of color. These comparisons sharpen your ability to distinguish between styles.
Comprehensive modern art history provides context for understanding how styles evolved and influenced each other. Modern movements often developed as reactions against or extensions of previous styles, creating a rich tapestry of artistic innovation that continues evolving today.
Technology’s Future in Art Analysis
The intersection of art and technology continues expanding, with new applications emerging regularly. Machine learning algorithms become increasingly sophisticated, capable of detecting subtle stylistic influences and cross-cultural artistic connections. These developments promise to revolutionize how we understand art history and cultural exchange.
Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies offer immersive ways to experience art styles, allowing viewers to step inside paintings or see artworks in their original contexts. These tools make art education more engaging and accessible, particularly for students who learn better through interactive experiences.
The integration of scientific authentication methods with traditional art historical analysis creates more robust approaches to understanding artworks. This combination of human expertise and technological precision represents the future of art scholarship and appreciation.
Upload Your Painting
Upload a file or drag and drop
PNG, JPG, GIF up to 10MB
Style Analysis
Analyzing your masterpiece…
📝 Review
💡 Style Suggestions
Upload a painting to see a detailed analysis of its composition, color palette, brushwork, and overall mood. Get constructive feedback to help you grow as an artist.
Discovering Hidden Meanings and Connections
Art styles often contain layers of meaning that extend beyond aesthetic considerations. Understanding these deeper connections helps appreciate how artists responded to social, political, and cultural changes throughout history. The evolution of artistic expression reflects broader human experiences and concerns.
AI analysis reveals patterns and connections that might escape human observation, such as subtle compositional similarities between artists who never met or worked centuries apart. These discoveries suggest universal principles of visual organization that transcend cultural boundaries and historical periods.
The ability to decode the visual language of art enhances both scholarly research and personal enjoyment. Whether analyzing a Renaissance masterpiece or a contemporary work, understanding stylistic elements provides tools for deeper appreciation and more meaningful engagement with artistic creation.
Learning to enhance your art appreciation skills involves developing both analytical and emotional responses to artworks. Technical knowledge of brushwork, composition, and color theory combines with personal interpretation and cultural understanding to create rich, meaningful experiences with art.
The comprehensive guide to painting movements demonstrates how understanding artistic development enhances appreciation for individual works. Each movement built upon previous innovations while responding to contemporary concerns, creating the rich tapestry of artistic expression we enjoy today.
Museums and galleries increasingly use technology to help visitors discover hidden meanings in masterpieces, providing interactive experiences that reveal symbolic content, historical context, and artistic techniques. These innovations make art more accessible to diverse audiences while preserving scholarly rigor.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I learn to identify different art styles quickly? Start with major movements like Renaissance, Baroque, Impressionism, and Cubism. Focus on key characteristics: Renaissance uses linear perspective and realistic proportions, Baroque emphasizes dramatic lighting, Impressionism features visible brushstrokes and natural light, while Cubism fragments objects into geometric shapes.
What makes AI analysis of art styles different from human analysis? AI can process thousands of data points simultaneously, detecting subtle patterns in brushstrokes, color composition, and texture that human eyes might miss. However, AI lacks cultural context and emotional understanding that human experts provide, making the combination of both approaches most effective.
Can AI completely replace art experts in style identification? No, AI serves as a powerful tool that enhances human expertise rather than replacing it. While AI excels at pattern recognition and data analysis, art experts provide cultural context, historical knowledge, and interpretive skills that remain essential for complete understanding.
How accurate is AI in detecting art forgeries? Modern AI systems achieve 90-95% accuracy in detecting forgeries when combined with other authentication methods. The technology analyzes brushstroke patterns, aging characteristics, and material composition to identify inconsistencies that suggest forgery.
What should beginners focus on when learning about art styles? Begin with understanding the historical context of major movements, then practice identifying key visual characteristics. Study how different artists solved similar problems and notice how styles evolved over time. Regular museum visits and comparing similar works from different periods accelerate learning.



