French pastel painting techniques transformed a simple sketching medium into a sophisticated art form that captured the light, emotion, and elegance of 18th-century France. From the delicate touch of Rosalba Carriera to the expressive motion of Edgar Degas, these artists reshaped the medium and left an enduring legacy that continues to inspire creators today.
Learn About:
- The 18th century marked the golden age of French pastel art.
- Artists like Maurice Quentin de La Tour and Vigée Le Brun revolutionized portraiture with pastel.
- Techniques include layering, blending, and careful use of fixatives for longevity.
- Pastel evolved from a preparatory sketch tool into a refined fine art medium.
- Modern artists still draw inspiration from French pastel masters.
🎨 What Makes French Pastel Painting Techniques So Special?

French pastel painting techniques balance precision with freedom. Artists used pastels to capture soft fabrics, lifelike skin tones, and shimmering light with a luminosity few other mediums could achieve. Applied directly to textured paper, the pure pigment created rich, velvety surfaces perfect for Rococo portraiture.
🕰️ The Golden Age of Pastel in France
Before the 18th century, artists used pastels mainly for quick studies. But during the Rococo art movement, French painters transformed it into a celebrated fine art medium. Rococo’s pastel color palette and lighthearted spirit were perfectly suited to this new form of expression.
Notable Masters of the Era
| Artist | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Rosalba Carriera | Introduced pastel portraiture to France, inspiring generations of artists. |
| Maurice Quentin de La Tour | Mastered the art of psychological realism through delicate pastel portraits. |
| Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin | Used pastels to enrich still lifes and intimate domestic scenes. |
| Jean-Étienne Liotard | Achieved remarkable realism through meticulous layering techniques. |
| Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun | Brought elegance and emotion to neoclassical pastel portraiture. |
“Pastel is the purest expression of light and color, unmediated by liquid or brush.”
Maurice Quentin de La Tour
🧠 Understanding French Pastel Painting Techniques
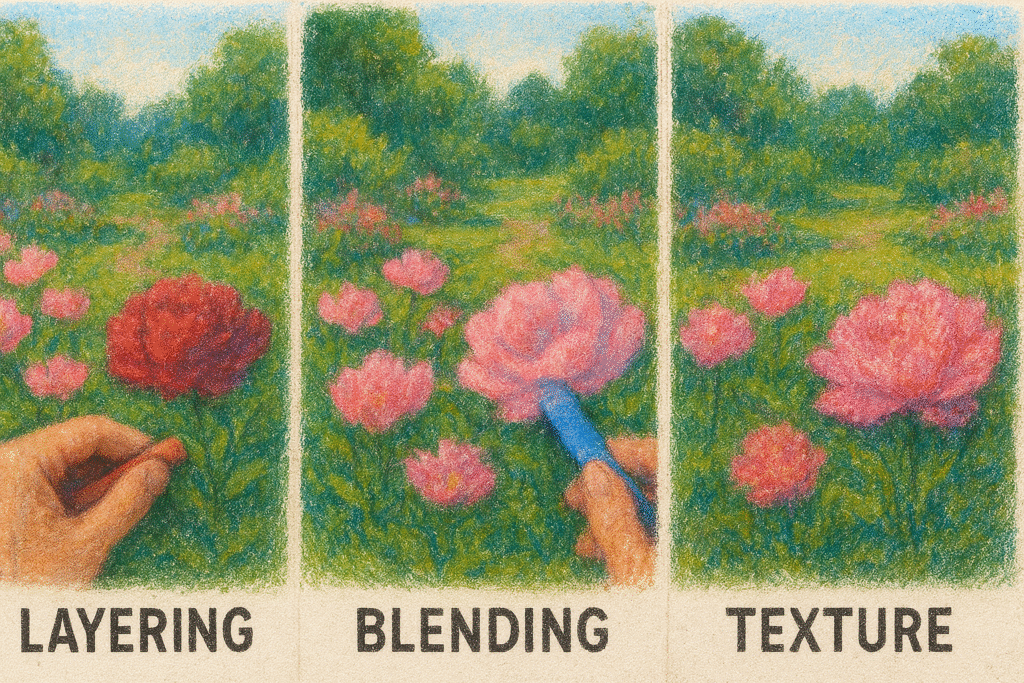
To master pastel, French artists united deliberate technique with expressive spontaneity. The essential elements—layering, blending, and texture—worked together to produce lifelike, radiant results.
Layering and Blending
Artists sketched with hard pastels and built depth with softer ones. They used fingertips, paper stumps, or cloths to blend hues subtly, ensuring smooth transitions while preserving the paper’s texture.
Surface Preparation
High-quality, textured paper—often sanded or handmade—was critical. French painters favored blue or gray paper for balancing warm skin tones and enhancing color contrast.
Fixatives and Preservation
Natural fixatives such as gum arabic helped reduce smudging. Yet, artists applied them sparingly to retain the soft, powdery glow that defines pastel art.
Capturing Emotion and Light
More than realism, the goal was to convey presence and emotion. Gentle highlights around the eyes and lips gave portraits warmth and vitality that oil paintings often lacked.
🏛️ The Pastel Revolution: From Sketch to Fine Art
The French Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture formally recognized pastel as a fine art medium in the 18th century—a landmark achievement. Exhibitions at the Salons of Paris soon featured pastel portraits that rivaled oils in sophistication and popularity.
Pastel became the language of intimacy, favored for portraits of nobility, families, and lovers. Its immediacy and tenderness reflected the essence of Rococo France.
For more on Rococo aesthetics, see Exploring Rococo Color Palettes in Painting.
💀 Decline and Revival: Degas and Beyond
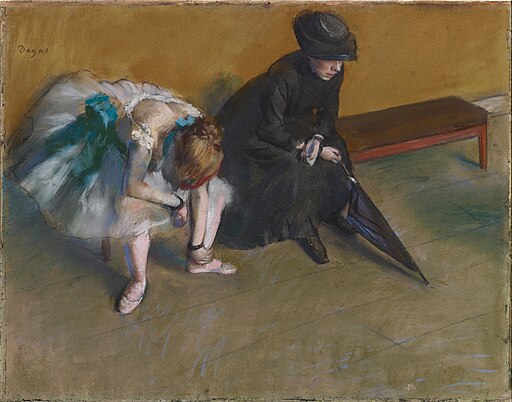

After its 18th-century peak, pastel briefly faded from prominence. Then Edgar Degas revived it in the 19th centuy, revolutionizing its use through bold strokes, layering, and expressive movement.
Degas’s dancers, glowing with dynamic color and light, became symbols of Impressionist pastel art. His innovations inspired artists like Mary Cassatt and Odilon Redon, sparking a pastel renaissance that shaped modern art.
Learn more about Impressionist techniques in Impressionist Drawing Techniques for Beginners.
🧰 Modern Lessons from French Pastel Painting Techniques
Bridging historical mastery and modern artistry, today’s pastelists can apply timeless French techniques:
- Use soft pastels for luminous color and expressive texture.
- Choose textured pastel paper in neutral shades.
- Build up tones from dark to light through gradual layering.
- Apply fixatives lightly to preserve vibrancy.
For supply tips, visit Best Pastel Paper for Realistic Drawings.
📺 Recommended Video: The Magic of French Pastels
French pastel painting techniques continue to enchant artists worldwide, blending tradition with innovation. Whether you’re drawn to La Tour’s grace or Degas’s dynamism, mastering these timeless techniques opens a vivid world of light, texture, and emotion—just as it did for the French masters centuries ago.
❓FAQ: People Also Ask
Q: What is the history of pastels in France?
A: Pastels rose to prominence in 18th-century France during the Rococo era, when artists began using them for refined, luminous portraits.
Q: Who are some famous French pastel artists?
A: Masters include Maurice Quentin de La Tour, Rosalba Carriera, Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin, and Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun.
Q: What techniques did French artists use with pastels?
A: Core techniques involved layering, blending, and careful fixation to achieve lifelike, glowing effects.
Q: How did pastels become popular in the 18th century?
A: Their ability to capture softness and light made them ideal for Rococo portraiture and favored by France’s elite.
Q: Did Edgar Degas use pastels?
A: Absolutely. Degas revived the medium in the 19th century, using it to portray movement and atmosphere in his iconic ballerina paintings.